- Posted on 06 May 2015 9:53 am
Jim Corbett holds the reputation of being a first national park in India. Corbett is an ideal home to a wide variety of wildlife species. Earlier it was a wildlife delight but now animals like tiger elephants, bears, and crocodile are hard to sight. The park is greatly revered by local people for killing animals that preyed on people. Corbett eventually shot more wildlife with his camera than with his gun and became a prominent voice for conservation. Demand for animal parts is the biggest threat to the survival of wildlife. Poachers are killing these animals to get their bones, teeth, claws and skin so that they can be sold for thousands of dollars in the illegal wildlife market.
To maintain the ecological balance and prevent tigers from extinction, conservation activities have become very important in this national park. Corbett national park, which was once the abode of many species, has just 2226 tigers in its jungle. Throughout the country, good efforts are being made by the central and state government to preserve the wild animals in Jim Corbett National Park. Following initiatives has been started by central and state government for the protection of animals in Jim Corbett National Park:
1. Project Tiger
Established In 1973 by the Government of India, Project tiger is a tiger conversation initiative launched under the guidance of Mrs. Indira Gandhi, then Prime Minister of India. The project was practices for the first time in Dhikhala Zone of Jim Corbett National Park in 1973. The decrease in the tiger population was the reason behind the establishment of the initiative. In the 20th century, the tiger population in India was around 20, 000-40,000; however in 1972 the count was reduced to 1800 tigers. Moreover, the tiger population was reduced to 268 in 1973.
Reasons Behind Reduction of Tiger Population
- Hunting and Poaching
- Deforestation for developmental activities
- The damage and disintegration of wildlife locale under mounting human wants for fodder, fuel and drawing out of non-timber woods products.
Objectives of Project Tiger
- To limit the reasons behind the certain reduction of tiger habitat and to mitigate them by suitable management.
- o reduce the dependency of local people on tiger reserve resources for eco-development
- To ensure a viable population of tigers for economic, scientific and cultural values.
Steps Taken by the Government
- Tiger Protection Force comeback was initiated to combat poachers and funds were given to villagers who leave in the wildlife reserve to avoid animal-human conflict.
- The project was administered by the National Tiger Conservation Authority. Overall it was administered by steering committee headed by a director.
- Wireless communication systems and outstation patrol camp were implanted within the tiger reserve.
- Each and every tiger reserve is managed by a Field director (rank of conservator of Festival)
Result
More wildlife reserves were brought under the canopy of Project Tiger. As a result, the tiger population was increased to over 4,000 in 1989 census. However, in 1983, there was a significant dip in Tiger population due to increasing in poaching cases.
Current Status
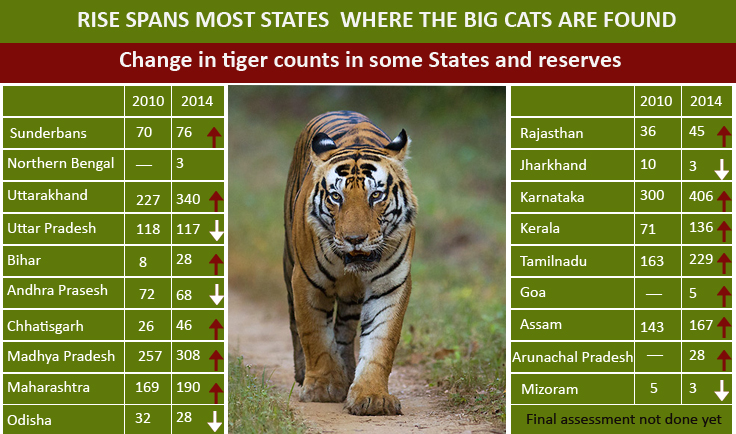 The 2006 census had estimated that there were 1,411 tigers, without including any from the Sunderbans. In 2010, there was a 12% rise in the tiger population. Presently in 2015 there are 43 Tiger reserves in India, and as per the census report of January 20, 2015 the tiger population is 2226.
The 2006 census had estimated that there were 1,411 tigers, without including any from the Sunderbans. In 2010, there was a 12% rise in the tiger population. Presently in 2015 there are 43 Tiger reserves in India, and as per the census report of January 20, 2015 the tiger population is 2226.
2.Crocodile Conservation Project
In India, crocodiles are both revered and loathed as some consider them religious and others consider them a menace. In 1970, only 100 Gharial crocodiles survived in the wildlife sanctuary in India. The project was first initiated in 1976 in of Jim Corbett National Park with an aim to protect the crocodiles of the nation, namely, freshwater crocodile, gharial crocodile, and saltwater crocodiles. The project aims to ensure the increase, the increase in the numbers through breeding.
Objectives of Crocodile Conservation Project
- Eco logical development
- Captive breeding of the species
- Collecting the eggs of crocodile from regular haunts, ensuring crosshatching and nurturing of crocodiles in captivity to lessen mortality because of the natural predators and lastly released into the wild.
Steps Taken by the Government
- Veterinary care
- arious studies and literature were introduced to create awareness amongst the masses.
- The Gharial Rehabilitation Project formed a subunit of the umbrella Crocodile Conservation Project.
- Sixteen crocodile rehabilitation centres and 11 crocodile centuries were established.
- To locate, establish and manage a series of crocodile rehabilitation centres and sanctuaries in suitable habitats.
Result
By the time project ended, around 250 gharial crocodiles were released in Ramnagar River in the Corbett region between the years 1982 to 1994.
3. Project Elephant
Project elephant was launched with an aim to increase the elephant population by providing financial and technical aid to major elephant bearing states in the country. The project was launched in the year 1991-1992. The Project elephants were further launches in 13 states and Union Territories, i.e. Andhra Pradesh, Arunachal Pradesh, Assam, Jharkhand, Karnataka, Kerala, Meghalaya, Nagaland, Orissa, Tamil Nadu, Uttarakhand, Uttar Pradesh and West Bengal with an aim, Uttar Pradesh and West Bengal with an aim to protect the decline in number of tiger population.
Objectives of Project Elephant
- Eco development of elephant habitat’s
- To provide more veterinary care to elephants
- Research on management issues related to elephants
- Strengthening of initiatives related to protection of wild elephants- poaching and unnatural cause of death.
- To Increase the population of tusked elephants.
- oderating impact of human and domestic stock activities in crucial elephant habitats
- To prevent human actions in the elephant haunts for their protection
Steps Taken by the Government
25 elephant reserves were made in India – West Bengal, Jharkhand, Orissa, Arunachal Pradesh, Assam, Nagaland, Meghalya, Karnatka, Tamil Nadu, Kerela, Andhra Pradesh and Karnatka.
Current Status
10 elephant reserve in India are finally implementing MIKE (Monitoring of Illegal killing of Elephants)
Some Other Conservation Schemes and Plans
Multiple other projects were started in Jim Corbett National Park for the sustainable development and protection of animals:
Interim Relief Scheme
There are around 250 villages and 25 Gujjar tribes located in and around the buffer zone of Corbett wildlife reserve. The major conflict originated when here is a loss of livestock due to wildlife predators and damage of crop due to wild herbivores. As per this scheme, the forest departments give monetary compensation to those villagers whose cattle’s are killed in the buffer zone area. The villagers are supposed to inform the officers in Dhikuli and Rathuadhab area in case of any attack on the cattle. Interim Relief Scheme (IRS) provides on-the-spot monetary help to the affected villagers. The team takes control of the situation and pay the applicable interim relief to the villagers.
Cattle Vaccination Camps
In Corbett, sometimes it rains like cats and dogs; hence there is an increase in cases of mouth and foot diseases. There is a risk of such diseases being transferred to the wild animals of Corbett. To avoid such deplorable situation, around 6000 livestock’s were vaccinated under this camp.
The Corbett Foundation
Corbett Foundation comprises a set of devoted men and women, who are dedicated to the conservation of wildlife and nature’s bounty, and to the accomplishment of the goal that human beings and nature must breathe together in coherence. The Corbett foundation is working rigorously for the conservation of wildlife in Jim Corbett National Park. Tiny initiatives taken by the government in which citizens can take part are:
- Nature Camps
- Nature Walks
- Signature Camps
- Tiger Programs
- Presentation on tiger conservation in schools
Conservation efforts in Corbett are visibly focused to conserve the exotic wildlife of this park. The effect of these efforts can be clearly seen if you visit this spellbinding empyrean for wildlife! The conservation of wildlife species is thoroughly important for the ecological equilibrium. Take a part in these conservation events if you want the safeguard the flora and fauna of India.
Also Check:




